In pursuit of its visionary aim to lead the charge towards climate neutrality by 2050, the European Union (EU) has embarked on a transformative journey. One of its recognizable pioneering initiatives to curb the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions has materialized since 2005 when it implemented the carbon pricing mechanism on EU corporations through the EU ETS cap-and-trade system. This system, however, has brought about disadvantages to manufacturers in the EU, leading to unfair competitive edge for companies in regions with more relaxed environmental regulations.In 2019, the European Green Deal was established to further enhance and accelerate the EU’s climate and sustainability efforts. The European Green Deal encompasses a wide range of strategies and measures, among which stands the Cross-Border Carbon Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), which in one way will assist the EU in realizing the climate neutrality goal, and in another way will protect EU industries from unfair competitions caused by higher environmental costs.
CBAM, an acronym that carries immense significance for businesses, policymakers, and stakeholders around the globe, represents a pivotal component of the EU’s commitment to addressing climate change. As we delve into the intricacies of CBAM, we’ll unravel its impact on various industries, explore its timeline and implications, dissect the methods employed for emission calculation under CBAM standards, and delve into the ways manufacturers can measure, reduce, and offset emissions in the face of this transformative mechanism.
But CBAM is not just a challenge; it’s also an opportunity. As manufacturers navigate this dynamic landscape, financial institutions find themselves in a position to offer critical support and expertise. Together, they can accelerate the transition towards a cleaner, more sustainable future. Join us on this journey as we decode CBAM and illuminate the path forward in the realm of cross-border carbon adjustment.
What CBAM is
CBAM is a part of several initiatives introduced under the European Green Deal in support of the goal to be the first climate-neutral continent by 2050. Following that aspiration, the EU is imposing various carbon tax regimes on European manufacturers, and introducing CBAM to even the playing field and eliminate price advantage for imported products from regions where carbon measurements may not be as stringent. In short, CBAM is a carbon tax applied on carbon-intensive products imported into the European Union, the amount equivalent to the tax applied to identical domestic goods for the same amount of GHG being emitted.
During its initial phase, importers will only need to report the emissions associated with the imported goods. However, in the later stage of the regulation, importers will have to purchase CBAM certificates to compensate for any difference in the carbon price paid in the country of origin as compared to the carbon price charged to producers in the EU. To implement this framework, the following data will need to be collected by importers:
-
- Total quantity of imported products
- Carbon price paid for the product in the country of origin
- Actual direct and indirect emissions of GreenHouse Gas (“GHG”) of the imported products
CBAM’s scope and timeline
The CBAM’s transitional phase will be enforced from October 2023 to December 2025. During this phase, importers will only need to report the data related to their imports as specified above. No data verification or purchase of CBAM certificates is needed. The scope of products covered during this initial phase is 6 emission-intensive sectors which are more susceptible to a risk of carbon leakage: cement, aluminum, fertilizers, iron and steel, electricity, and hydrogen.
The permanent system will enter into force in January 2026. Importers will not only be required to report CBAM-related data, but will also be required to have the data verified by an accredited verifier and purchase CBAM certificates for any gap in the carbon price paid. An extension of the product scope for CBAM after the transitional phase will be reviewed to assess practicality and feasibility of such inclusion. Potential product categories to be covered in the second phase include organic chemicals, plastics, and ammonia. The extension is planned for full implementation by 2030.
Deconstructing calculation of GreenHouse Gas emission under CBAM
The scope of GHG emission under CBAM guideline closely aligns with the emission scope set out by the GHG Protocol Corporate Standard (“GHG Protocol”). The GHG Protocol distinguishes between three scopes of emissions:

Source: Zevero
- Scope 1 refers to GHG emission from own operation or asset that the company emits directly such as use of fossil fuel energy used in production or transportation
- Scope 2 refers to GHG emission that company indirectly emits from supporting business activities such as electricity used in air conditioning or lighting
- Scope 3 refers to all GHG emission that the company may induce along its value chain, such as providing financing to GHG emitting businesses or the purchase of office supplies that may emit GHG during production
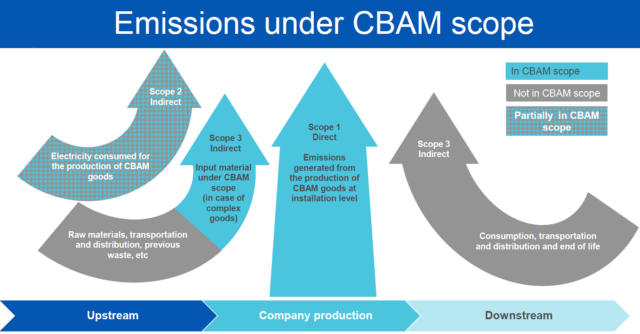
Source: European Commission
More specifically, direct emissions under CBAM equals to scope 1 emissions under the Greenhouse Gas Protocol, including GHG emitted directly during the production from combustion of fuel, or other byproduct emission incurred from material chemical reaction or heating and cooling process critical to the production. Accounting for the emission can either be based on actual measurement of the emission or calculation of emission using emission factor.
Indirect emissions under CBAM covers scope 2 and scope 3 of the GHG Protocol. Scope 2 reporting under CBAM only concerns electricity consumed during the manufacturing process of products, such as the lighting and air conditioning of the plant. As for scope 3, the biggest emission which is toughest to measure, CBAM only requires importers to report emissions from manufacturing of precursor input materials which are already under CBAM scope (cement, iron/steel, aluminum, hydrogen, and fertilizers). This initial stage does not necessitate complicated accounting of emission from activities like employee commuting or customer use of products. For more details on how to measure emissions for each sector, please find the European Commission’s guidance here.
CBAM: Shaping the Future of Trade and Sustainability – Implications for the Thai Economy
According to the Office of Industrial Economics, in 2022 Thailand exported $201 million of iron and $111 million of aluminum to countries in the EU. Although these only represented 1.3% of the total export in 2022, the scope of the extended CBAM covering other categories such as plastics will have greater impact as it accounts for $676 million or 2.4% of the total export.
All exporters for the above product categories will have a responsibility to report emissions to the EU, except products with value below €150 or products used in the military. After the transition period, Thai exporters will face an additional process of submitting the report to accredited verifier before the report will be deemed valid. They will also have to pay an additional cost of carbon tariff to the CBAM, net of any amount already paid in countries of origin.
Economic disadvantages to the Thai exporters
The price of carbon in the EU Emission Trading System, according to Statista, that will be used for carbon price reference in the initial implementation stage, has been fluctuating in the range of €80-€100 per ton of CO2 during the first half of 2023. The price is predicted to jump even higher when the full CBAM mechanism comes into effect as there will be more demand to purchase allowances under the EU ETS when the free allowances gradually phase out. One way to illustrate how this translates into economic disadvantage for Thai exporters is to calculate the difference in emission cost per ton of product between Thailand and other competing exporters. Examples of carbon tariff comparison for iron products and primary aluminum are shown in the table below.
| |
Iron: Thailand |
Iron: Global |
Iron: EU |
Aluminum primary: Thailand |
Aluminum primary: Global |
Aluminum primary: EU |
| 1Carbon price (USD/tCO2e) |
96.3 |
96.3 |
96.3 |
96.3 |
96.3 |
96.3 |
| 2Emission (tCO2e/ton) |
1.55 |
1.40 |
1.14 |
12.24 |
12.50 |
6.20 |
| Carbon Tariff (1*2) (USD) |
149.48 |
134.82 |
109.78 |
1,178.32 |
1,203.75 |
597.06 |
| Compare to Thailand (%) |
N/A |
-10% |
-27% |
N/A |
2% |
-49% |
As can be seen from the table above, Thai exporters are at a disadvantage in terms of higher carbon tariff. This is even more accentuated when compared to the EU manufacturers. This additional cost which will eventually lead to higher price charged to the European buyers, or the exporter will have to take profitability hit by absorbing the increased cost. This will likely shift Thailand’s export of CBAM goods to other locations outside of the EU in the short- to -medium term, given that there’s other buyers. However, manufacturers will need to gradually upgrade their production technology to a greener one to stay afloat as other countries like the United States will soon be implementing a similar mechanism to curb GHG emissions.
Current progress from Thai government agencies
In response to this significant change, the Department of Trade Negotiations (DTN), the Federation of Thai Industries (FTI), and the Thai Greenhouse Gas Management Organization (TGO) collaborated to host a seminar on CBAM. This seminar aimed to educate stakeholders and gather feedback regarding concerns during the initial implementation phase. Thai manufacturers have specifically requested support for reporting technology, permission to utilize Thai accredited verifiers for cost-effective report verification, and leniency in penalties for unintentional reporting errors during the adaptation phase. Currently, the DTN and FTI are engaged in discussions with EU representatives to explore potential solutions that can mitigate adverse impacts on Thai industries. We anticipate learning more about the outcomes in the near future.
Earlier this year, TGO made a significant stride by forging a collaborative partnership with the Ministry of Higher Education, Science, Research, and Innovation, in conjunction with five prestigious universities, including Chulalongkorn University and Thammasat University. Together, they are crafting an innovative curriculum tailored for sustainability professionals, equipping them with specialized knowledge in carbon footprint management and carbon credit utilization. This educational initiative aims to provide invaluable support for businesses as they transition seamlessly into the CBAM.
In addition to this pioneering educational endeavor, TGO is also developing a platform designed for embedded emission calculation. This platform serves as a vital tool to assist Thai manufacturers in accurately reporting carbon emissions, thereby ensuring compliance with CBAM regulations. The platform is now in the pilot testing phase with the active participation of several volunteer companies. Once fully realized, this forward-thinking initiative is poised to significantly reduce costs associated with emission reporting for Thai exporters.
Navigating the Transition: Challenges and Manufacturers and Opportunities for Startups
To remain competitive in the long term, manufacturers must address three key activities: measuring GHG emissions accurately, reducing GHG emissions effectively, and transacting carbon offsets. Each of these activities comes with its own implementation challenges, which startups can seize as opportunities to provide solutions.
1. Accurate Measurement of GHG Emissions
Accurate measurement of emissions serves as the bedrock of CBAM and any effective emissions reduction strategy, echoing the timeless wisdom of Peter Drucker: “You can’t manage what you can’t measure.” Worldwide, startups are diligently working to address this pivotal task by introducing innovative solutions through carbon accounting platforms. Prominent players in the carbon accounting space, such as Terrascope, RIMM, Unravel Carbon, and others, have emerged to tackle this challenge head-on. In Thailand, TGO is actively engaged in the development of an embedded emission calculation platform, poised to bring substantial advantages to Thai exporters upon its completion. However, it’s crucial to acknowledge that this endeavor is anything but straightforward, as it grapples with a multitude of formidable challenges. To shed light on this complexity, let us explore some of the most salient hurdles.
1.1 Lack of Data Integrity which mainly stems from lack of accuracy in measuring scope 3 emissions and difficulty standardizing data from various sources such as different equipment types and different factories. Nonetheless, integrating these features into carbon accounting tools can both improve accuracy and reduce standardization problems.
1.1.1 Carbon calculators using emission factors (EF) – unlocking the power of granularity: One of the fundamental hurdles in accurate GHG emission measurement lies in the granularity and availability of data. EFs are industry-specific proxies that can be used to estimate the actual carbon emission, such as the amount of raw materials used or the production method that the manufacturer adopts.
1.1.2 Integration across supply chain – connecting the dots: To achieve accurate GHG emission measurement, we must track a product’s entire lifecycle, extending beyond individual factories to encompass a web of suppliers. Integrated supply chain tracking is the key. Imagine a system where emissions data from every supplier seamlessly merges into a comprehensive picture. This integration ensures the accurate measurement of scope 3 emissions, offering a holistic view of a product’s carbon footprint.
1.1.3 Blockchain carbon ledger – enhanced data integrity: Data integrity is paramount in GHG emission measurement. Inaccuracies often arise due to a lack of trust and transparency. Enter blockchain technology, promising enhanced verifiability and transparency. A blockchain carbon ledger securely records, time-stamps, and links emission-related transactions across a decentralized network. This not only bolsters the credibility of reported data but also allows stakeholders to trace emissions data origins precisely.
1.2 Labor Intensiveness. Current practice of emission measurement involves extensive manual processing which leads to excessive costs and is prone to errors. However, these can be solved by using automation and technologies.
1.2.1 Integration with systems and equipment – the power of automation: One of the pressing challenges in current emission measurement practices is their labor-intensive nature, often leading to high costs and error-prone outcomes. By integrating carbon accounting systems with tools like IoT (Internet of Things), ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), or machinery, businesses can unlock the potential for automatic data retrieval based on activities. This shift towards automation significantly reduces the manual workload, making the process more efficient and cost-effective.
1.2.2 Optical Character Recognition – bridging the digital-physical gap: Physical documents have long posed challenges in the realm of GHG emission measurement due to their manual processing requirements. However, optical character recognition (OCR) technology provides a compelling remedy. OCR can automatically transform physical documents into digital formats, opening the door to efficient, automated processing for emissions calculations. By digitizing these documents, the entire process becomes faster, more accurate, and cost-effective.
2. Effective and Sustainable Emissions Reduction
Once emissions are accurately measured, manufacturers must reduce emissions during their processes to lower carbon tariff payment. However, this is hampered by technical limitations and economic constraints.
2.1 Technical Limitations. Addressing technical limitations in emissions reduction calls for a multifaceted strategy. Manufacturers grapple with three core challenges: the search for durable green material alternatives, the need for an ample supply of renewable energy for energy-intensive industries, and the imperative to mitigate high-emission manufacturing processes. In response, ongoing research and studies are relentlessly pursuing innovative solutions that encompass various aspects of emission reduction.
2.2.1 Innovative materials – pioneering more sustainable inputs: Promising alternatives are emerging, exemplified by initiatives like ELYSIS‘ development of inert anodes for aluminum smelting or HARBOR Aluminum‘s dedication to recycled materials. These innovative materials aim to reduce emissions and improve sustainability across industries.
2.2.2 GHG compound mitigation – preventing emissions at the source: Another avenue of exploration is the development of technologies that mitigate the formation of greenhouse gas compounds during manufacturing processes. Initiatives such as Analytics Shop‘s work on nitrification inhibitors in fertilizers and Hybrit‘s pursuit of hydrogen reduction in iron ore processing hold promise in this regard.
2.2.3 More efficient facilities management – smarter operations: Smart buildings, pioneered by companies like AltoTech, TIE-Smart, and Zenatix, are reshaping facilities management by optimizing energy usage and reducing emissions, contributing to sustainable manufacturing.
2.2.4 Use of renewable energy – filling the energy gap: Addressing the shortfall in renewable energy supply, especially for energy intensive industries, is critical. According to the Office of Natural Resources and Environmental Policy and Planning, Thailand, for instance, lags behind the EU, with only 11% of its energy consumption sourced from renewables in 2021. Thailand still has a lot of room to grow when compared to almost 40% in the EU. Providers like Clover Power and First Korat Wind offer renewable energy solutions that can help bridge this gap.
2.2.5 GHG capture technologies – seizing emission: Manufacturing plants are notorious sources of greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), which is a primary contributor to global warming. By capturing these emissions at the source, we prevent them from being released into the atmosphere and exacerbating the greenhouse effect. Solutions such as carbon capture, utilization, and storage by Technip and Linde, along with direct air capture technologies developed by companies like Carbon Engineering and Climeworks, play a crucial role in capturing and mitigating emissions right at their source.
2.2 Economic Constraints: The economic constraints that often accompany the adoption of new and cleaner technologies pose significant challenges for manufacturing businesses in their efforts to reduce their carbon footprint. These constraints can manifest as high upfront investment costs, the need for workforce reskilling, and downtime of factories. However, manufacturers have several valuable options to navigate these economic challenges while advancing their sustainability objectives:
2.2.1 Sustainable Finance – accessing transitionary funding: One key strategy is to tap into sustainable finance options. Providers like GoParity and BluePath Finance offer gateways to sustainable financing, facilitating access to the capital necessary for investing in cleaner technologies. This approach not only aids in overcoming the initial financial hurdle but also aligns with broader sustainability goals.
2.2.2 Data Analysis and Tools for Emission Optimization – maximizing return on impact investment: In a world of budget constraints, where companies must make strategic decisions about where to invest for emissions reduction, data analysis and specialized tools play a pivotal role. The goal is to pinpoint precisely where within operations every dollar spent will yield the most significant reduction in carbon emissions. This approach empowers business owners to prioritize their budget effectively and make informed decisions about which areas to target for maximum impact on their carbon footprint.
2.2.3 Supply Chain Analysis – connecting the dots: Supply chain analysis plays a critical role in managing economic constraints while reducing carbon footprints. Manufacturers can seek out low-emission suppliers for raw materials within the scope of the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM). Companies like Pantas and Terrascope specialize in supply chain analysis, helping manufacturers make informed decisions about sourcing materials from environmentally responsible suppliers.
3. Transaction of Emission Offsets
As manufacturers progress through the carbon reduction journey, the third crucial step involves addressing the remaining emissions either by making carbon tariff payments or through the purchase of carbon credits. While both options require a financial commitment, payments for carbon emissions to local organizations that support green initiatives within their own country is often the preferred choice. However, this stage introduces complexities that demand specialized knowledge to navigate effectively. Additionally, the EU has yet to announce clear regulations on framework for carbon credit purchase. We must closely monitor the forthcoming frameworks set to be released in the second quarter of 2025.
If permitted by regulation, the process of purchasing carbon credits operates within specific parameters. Manufacturers are likely to be permitted to purchase carbon credits, which can be deducted from their overall carbon tariff liability. The exact quantity and conditions of allowable carbon credits is subject to CBAM regulations and may vary based on factors such as industry type and historical emissions records.
Providers specializing in carbon credit exchanges, such as T-VER and Climate Impact X, along with renewable energy credit exchanges like Innopower, typically offer comprehensive guidelines and training to support manufacturers throughout this journey. The official CBAM website is also a valuable resource for staying informed about the latest terms and regulations updates. These resources help businesses navigate the complex landscape of carbon offset transactions, ensuring compliance with CBAM requirements and contributing to their sustainability goals.
Financial institutions’ roles to facilitate smooth transition to CBAM
As manufacturers embark on the multifaceted journey of carbon reduction and compliance with the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), they encounter a diverse range of challenges. From the meticulous measurement of greenhouse gas emissions to the implementation of innovative technologies for emission reduction, and finally, to navigating the complexities of carbon offset transactions, each step poses unique hurdles.
However, at the heart of these challenges lies a common thread: the need for financial resources to support the development and adoption of sustainable climate technologies. In the initial phases of measuring and reducing emissions, manufacturers often grapple with the financial burden of investing in new tools, processes, and infrastructure. This financial strain can be a significant barrier to progress.
On the other end of the spectrum, when it comes to carbon offset transactions, manufacturers face challenges rooted in knowledge gaps. The intricacies of purchasing carbon credits, understanding CBAM regulations, and effectively managing emissions offset strategies can be daunting without the necessary expertise.
This is where financial institutions (FIs) play a pivotal role in facilitating a smooth transition into CBAM. FIs are well-positioned to address both of these critical challenges.

Addressing Funding Challenges for Climate Technologies:
1. Provider of Low-Interest Green Loans: FIs can act as a lifeline by offering low-interest green loans to both retail customers and corporations looking to fund the development and implementation of climate-friendly technologies. Establishing clear eligibility criteria and monitoring guidelines for the use of these funds ensures they are directed toward emission reduction effectively. FIs can even collaborate with government agencies and regulators to design more favorable incentives at a policy level, specifically tailored to manufacturers under CBAM transition. Many banks worldwide are already participating in this green loan initiative, for example, Deutsche Bank, OCBC, BBL, and KBank.
2. Investor in Climate Tech Startups: FIs can further accelerate technology development by investing in climate tech startups through corporate venture capital arms. These investments not only inject capital but also foster innovation and growth within the climate tech sector. Examples of FIs who already committed funds for impact investing include HSBC and KBank.
3. Manager of Sustainability Funds: FIs have the capability to manage sustainability-focused funds designed for public investment. These funds can target companies that are actively involved in climate tech development or adhere to sustainability best practices. Such investments promote the growth of climate-friendly technologies and sustainable practices. FIs who are already in the space include UOB, Blackrock, SCB, and KBank.
4. Partner of Climate Tech Solution Providers: Collaborating with climate tech solution providers, FIs can offer emission reduction solutions, such as carbon accounting systems, at accessible prices to their clients. These partnerships expand the availability of essential tools for manufacturers seeking to reduce emissions.
Addressing Knowledge Gaps for Carbon Offset Transactions:
1. Trainer and Educator: FIs can organize knowledge-sharing sessions and seminars focused on CBAM and other sustainability-related topics. These educational initiatives empower manufacturers with the knowledge required to navigate the complexities of carbon offset transactions effectively. Examples of FIs who are already active in sharing knowledge with the public include Commonwealth Bank of Australia, Santander Bank, and KBank.
2. Sustainability Advisor to Clients: FIs can equip their relationship managers with expertise in climate tech and CBAM. This enables them to provide informed advice to clients and guide them toward valuable sources of information and third-party climate tech solution providers. FIs such as HSBC and KBank have already pledged resources to help advise clients in this field.
3. Resource Hub for Trustworthy Climate Tech Solutions: Leveraging their knowledge and extensive networks, FIs can curate a list of trustworthy third-party climate tech solution providers. Conducting due diligence on these providers and referring them to clients in need of emissions reduction solutions ensures that manufacturers receive reliable and effective assistance.
Closing thoughts
In the approaching era of CBAM, manufacturers are not embarking on this transformative journey alone. There is a collective effort involving various stakeholders, including business owners, SMEs, startups, investors, and financial institutions, all gearing up to navigate the changing landscape. The challenges and opportunities presented by CBAM are not isolated to a single industry or region; they resonate globally.
Startups, in particular, stand at the forefront of innovation to assist companies during this transition. Their pioneering spirit and fresh perspectives can play a crucial role in addressing the complexities of CBAM. By leveraging the solutions and expertise of these startups, manufacturers can avoid the need to reinvent the wheel, accelerating their path to compliance and sustainability.
While the initial impact of CBAM may seem modest for regions less reliant on carbon-intensive exports to the EU, it’s essential to recognize the broader shift occurring worldwide. The cross-border carbon tax era is dawning, with countries like the United States considering similar measures through legislation such as the Clean Competition Act, which will impose carbon taxes on carbon-intensive products imported into the country. This legislation is planned for enforcement in 2024. Iron products exported to the US in 2022 totaled $4,510 million and aluminum products totaled $1,433 million. This global movement towards carbon pricing underscores the inevitability of higher costs associated with emissions.
Manufacturers, in response, are already redirecting their efforts towards greener manufacturing technologies. While this shift may initially impact costs, it serves as a crucial step towards a more sustainable future. Ultimately, these higher costs will be reflected in the products reaching end consumers. As awareness grows and preferences evolve, the public is increasingly inclined to favor low-carbon products, paving the way for a more environmentally conscious marketplace.
In embracing CBAM and its associated challenges, there is a collective opportunity for positive change. Manufacturers, startups, investors, and financial institutions are poised to collaborate in shaping a cleaner and more sustainable future. As we collectively adapt to this new era, the transition towards a low-carbon economy offers not just challenges but a compelling vision of a greener, more environmentally responsible world.
Author: Benjamas Tusakul
Editor: Woraphot Kingkawkanthong
References
-
- https://www.consilium.europa.eu/en/press/press-releases/2022/03/15/carbon-border-adjustment-mechanism-cbam-council-agrees-its-negotiating-mandate/
- https://kpmg.com/xx/en/home/insights/2022/08/carbon-border-adjustment-mechanism-impacts.html
- https://taxation-customs.ec.europa.eu/carbon-border-adjustment-mechanism_en
- https://www.pwc.ch/en/insights/tax/eu-deal-reached-on-the-cbam.html
- https://www.europarl.europa.eu/legislative-train/package-fit-for-55/file-carbon-border-adjustment-mechanism
- http://env_data.onep.go.th/reports/subject/view/128
- https://watchwire.ai/5-carbon-accounting-challenges-and-how-address-them/
- https://www.pwc.com/m1/en/services/tax/me-tax-legal-news/2023/eu-carbon-border-adjustment-mechanism.html
- http://www2.ops3.moc.go.th/
- https://mgronline.com/business/detail/9660000048165
- https://carboncredits.com/congress-introduces-us-cbam-clean-competition-act/
![]()
![]()
![]()